![]() With the popularity of PokemonGo, it was inevitable that a malware developer would create a ransomware that impersonates it. This is the case with a new Hidden-Tear ransomware discovered by Michael Gillespie that impersonates a PokemonGo application for Windows and targets Arabic language victims.
With the popularity of PokemonGo, it was inevitable that a malware developer would create a ransomware that impersonates it. This is the case with a new Hidden-Tear ransomware discovered by Michael Gillespie that impersonates a PokemonGo application for Windows and targets Arabic language victims.
The Bleepingcomputer site seems to have developed itself as the premier site that reports on new ransomware strains. Larry Abrams wrote about this strain: "On first glance, the PokemonGo ransomware infection looks like any other generic ransomware infection. On closer look, it is apparent that this developer has put in extra time to include features that are not found in many, if any, other ransomware variants. These features include adding a backdoor Windows account, spreading the executable to other drives, and creating network shares. It also appears that the developer isn't done yet as the source code contains many indications that this is a development version."
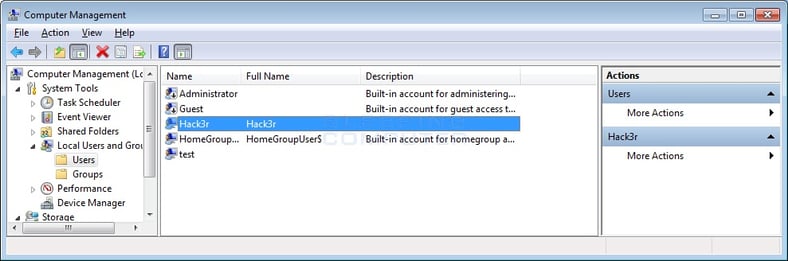
PokemonGo Ransomware will create a user account called Hack3r
"When installed, the PokemonGo Ransomware will create a user account called Hack3r and adds it to the Administrators group. It then hides this account from being seen on the Windows login screen by configuring a Windows registry key.
Another feature is that it contains a function that will create a network share on the victim's computer. It is currently unknown what this share will be used for as most shares would be blocked a victim's router or firewall. This function is currently not being used by the program.
More detail about the file types attacked, other features still in development, countries targeted and more at the blog post at Bleepingcomputer.




