![[EYE OPENER] The Ransom Payment is Only 15% of The Total Cost of Ransomware Attacks](https://blog.knowbe4.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Cyber%20Attacks%20Up%20125%25%20Ransomware%20Tops%20List.jpg?width=330&name=Cyber%20Attacks%20Up%20125%25%20Ransomware%20Tops%20List.jpg) As the number of ransomware attacks has increased 24% over the previous year, security researchers estimate the total associated attack costs to be just over 7 times higher.
As the number of ransomware attacks has increased 24% over the previous year, security researchers estimate the total associated attack costs to be just over 7 times higher.
Every time there’s a news story about a ransomware attack, there’s so much focus put on the ransom itself – this is probably due to the fact that the payment can be easily quantified; whether it be the amount asked for or the amount paid.
We’re all aware of the practical costs a business has to absorb should it become a ransomware victim – but those costs are seldom (if ever) revealed, leaving us guessing as to how much a ransomware attack actually costs the victim organization.
But new compiled and analyzed data from researchers at Check Point and Kovrr shows that the ransom amount is but a small portion of the total real cost of surviving a ransomware attack. When considering the losses in response and restoration costs, legal fees, monitoring and decreases in revenues, real-life cost data from actual organizations that were hit with ransomware paints the picture that ransomware is so very much more expensive than the ransom alone.
According to Check Point, the average ransom payment is 48.6% of the initial ransom demand – which is an average of about 2.82% of the victim’s annual revenue. So you can do the math: the average ransom paid is about 1.37% of annual revenue. But the overall costs are much, much more.
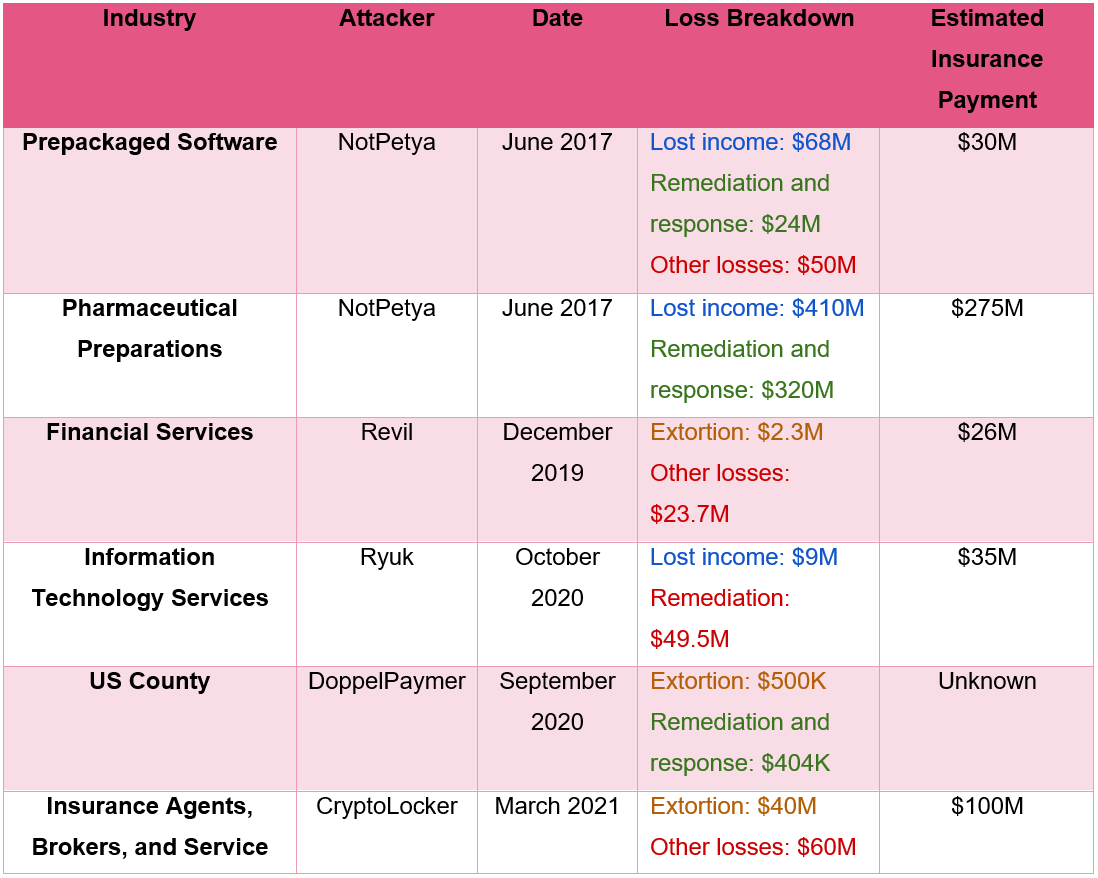
Take the following six example attacks (provided by Check Point) – note the “Extortion” values in comparison to the other costs:
According to Check Point, the average total cost of a ransomware attack is 7.083 times larger than the paid ransom. This means the average ransomware attack costs organizations an average of 9.7% of their annual revenues!!!
Now you do the math – which is more expensive: dealing with the financial repercussions of a ransomware attack or putting up a layered defense strategy that includes protecting the most likely (and least protected) aspect of your environment: your users?
Organizations that deploy new-school security awareness training as part of their security strategy significantly reduce their attack surface by nearly eliminating social engineering-based attacks as a possible initial ransomware attack vector.
%20(1).jpg?width=317&name=RogerMasterClass-FeatureImage%20(1)%20(1).jpg)





