 Last week, Fedor Sinitisyn, blogger and security researcher for Kaspersky posted something worrisome. He reported that the Angler Exploit Kit was delivering a new second-generation type of ransomware called CTB-Locker for "Curve-Tor-Bitcoin". Kaspersky identifies it as "Onion" because it uses the TOR network, Microsoft identifies the malware as Critroni.A.
Last week, Fedor Sinitisyn, blogger and security researcher for Kaspersky posted something worrisome. He reported that the Angler Exploit Kit was delivering a new second-generation type of ransomware called CTB-Locker for "Curve-Tor-Bitcoin". Kaspersky identifies it as "Onion" because it uses the TOR network, Microsoft identifies the malware as Critroni.A.
The Next CryptoLocker
Sinitisyn described Onion as the potential successor to CryptoLocker, and said that other malware used the anonymous TOR network though it was limited to banking malware families such as the 64-bit ZeuS.
Why Second Generation? 5 reasons:
- CTB-Locker is the very first Windows ransomware that uses the TOR network for its command & control (c&c) servers which makes it much harder to shut down.
- Traffic between the malware that lives on the infected machine and its c&c servers is much harder to intercept.
- Onion encrypts files using little-used and super strong Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman cryptography which makes decrypting it yourself impossible.
- Compresses files before encrypting them
- It was built as commercial crimeware, so it can be sold globally to other cybercriminals. The Bitcoin ransom can be specified, as can the extensions of the files that will be encrypted.
Once a PC is infected with Onion, the ransomware gives the victim detailed instructions on how to pay the Bitcoin ransom. Here is how the locking screen looks:
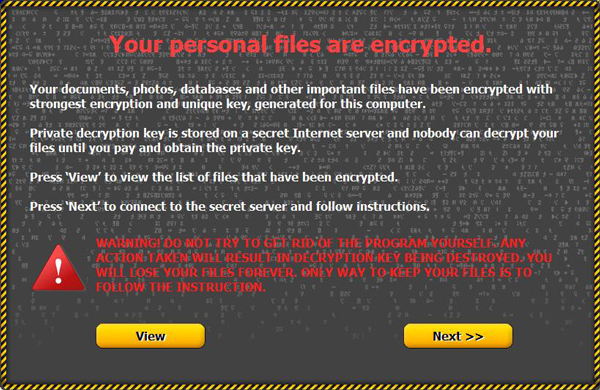
The fact that other cybercriminals are going to use this code will make it certain that the U.S. will be heavily targeted. Symantec's Internet Security Threat Report mentioned on page 6:
- Ransomware attacks grew by 500 percent in 2013 and turned vicious
- Scammers continued to leverage profitable ransomware scams where the attacker pretends to be local law enforcement demanding a fake fine of between $100 to $500.
- First appearing in 2012 these threats escalated in 2013, and grew by 500 percent over the course of the year.
More than ever it is needed to step your users through effective security awareness training before their files (or all the others on the file server) are being taken ransom. And (very obviously) you need excellent backup/restore software and test that frequently. KnowBe4 guarantees you that once all your users are trained and receive a simulated phishing attack once a month, we will pay your crypto-ransom if you get hit.
Related Pages: Ransomware





